Reproductive Medicine - Glossary and terms simply explained
Medical history
The medical history of the patient. This includes, among other things, all previous illnesses and surgeries and the cycle history, i.e. the duration and regularity of the menstrual cycle in the past.
Amenorrhea
When menstruation has not occurred after the age of sixteen (primary amenorrhea) or when menstruation has not occurred for more than three months (secondary amenorrhea).
Causes may include hormonal imbalances, pituitary gland disorders, certain genetic disorders, and severe psychological and/or physical stress.
Andrology
The science of male fertility disorders.
ART
Assisted Reproduction Techniques. This term includes all medical procedures of assisted fertilization (e.g., IVF, IVF/ICSI).
Aspermia
Medical term for the absence of an ejaculate despite the occurrence of an orgasm.
Assisted hatching
Assisted hatching is intended to make it easier for the growing embryo to leave the surrounding envelope ("zona pellucida") and thus increase the chance of implantation in the uterus.
Azoospermia
Refers to the complete absence of sperm (semen cells) in a sample of ejaculate.
Laparoscopy
A special camera is inserted into the abdomen through a small incision near the belly button to view the internal organs. Dye can then also be used to check the patency of the fallopian tubes. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.
Fertilization
The successful fusion of sperm and egg.
Chlamydia
A particular type of bacteria that often infects the reproductive organs, where it can be responsible for chronic inflammation.
Downregulation
Medicinal decoupling of the pituitary gland from the menstrual cycle in order to avoid premature triggering of ovulation in the treatment cycle.
Dysmenorrhea
Cramp-like pain during menstruation with a general feeling of illness. The cause may be anatomical (e.g. fibroids or polyps in the uterus), hormonal as well as psychological.
Dyspareunia
Medical term for pain during sexual intercourse. The cause may be organic (inflammation, infection, endometriosis) and/or psychological (listlessness, low arousal) disorders.
Ovaries
Twofold, plum-sized organs of the woman in which fertilizable eggs are produced. The ovaries produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
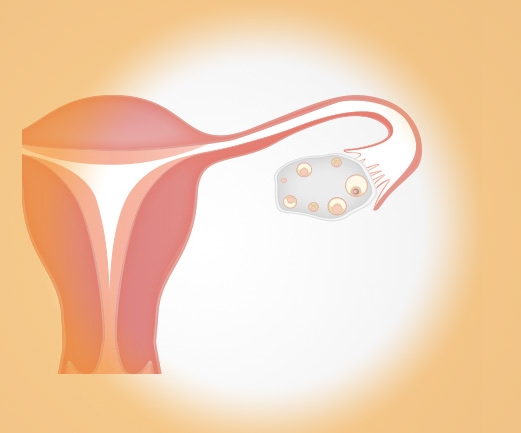
Fallopian tubes
Tubular ducts leading away from the uterus and ending in finger-like outgrowths called fimbriae on the ovaries. Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tubes.
Ovulation
The egg leaves the ovary and usually enters the fallopian tube.
Embryo
After fertilization of an egg by a sperm cell, the egg divides and from then on is called "embryo". This designation is maintained until the end of the third month of pregnancy. After that, it is called a fetus.
Embryo transfer
Also abbreviated as ET. Return of the embryo after IVF or IVF/ICSI using a small tube. The transfer is painless and takes place without anesthesia.
Endometriosis
Greek compound word: endo = inside, metra = uterus. Growths of scattered uterine mucosal cells in the abdomen. Often leads to period problems and infertility.
Endometrium
Uterine mucosa
Fern phenomenon
A change in cervical mucus observable by light microscopy before ovulation. The effect of estrogen changes the viscosity of the mucus. It absorbs more water, thus becoming thinner and particularly easy for sperm to penetrate. The dried mucus applied to a microscope slide forms a crystallization pattern similar to that of ferns.
Follicle
Fluid-filled follicles containing the oocytes. The follicles mature in the ovaries.
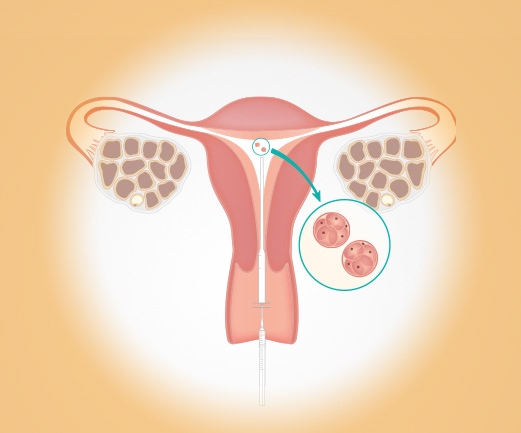
Follicular puncture
Ultrasound-guided egg collection using a hollow needle through the vagina. A short anesthesia is usually required.
Corpus luteum
Forms from the remnants of the follicle after ovulation and produces the female sex hormones progesterone and estrogen in the second half of the cycle (the implantation phase).
Gonads
Glands in which the reproductive cells are produced (in women the ovaries and in men the testes).
Habitual abortions
One speaks of habitual abortions (repeated spontaneous miscarriages) when several consecutive spontaneous miscarriages have occurred. Causes may be genetic (e.g., parental chromosomal abnormalities), anatomic (e.g., uterine malformations), hormonal (e.g., hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, luteal insufficiency), congenital, or infectious (chlamydia, toxoplasma).
Pituitary gland
Organ at the base of the skull, connected to the brain. It produces a variety of hormones that control many other organs, including ovarian and testicular function and thyroid and adrenal function.
Testicular biopsy
Removal of tissue from the testicle.
Idiopathic infertility
No clear explanation for the infertility can be found in either the woman or the man.
Implantation
Implantation of the embryo into the lining of the uterus.
Insemination
Also called IUI (intrauterine insemination). The sperm is injected into the uterus after appropriate preparation of the ejaculate.
IVF
In vitro - Latin: in a glass. In in vitro fertilization, after hormonal stimulation, oocytes are removed from the ovaries during a puncture. This is followed by fertilization by the sperm outside the body - therefore in vitro/in a test tube. The cells fertilized in this way are transferred back to the uterus as embryos a few days later.
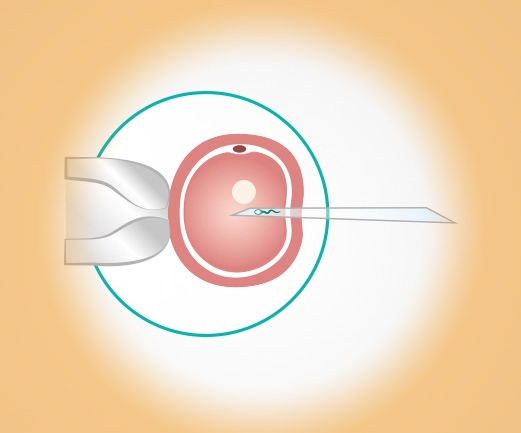
ICSI
In cases of very poor sperm quality, microinjection (ICSI = Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) becomes necessary in conjunction with IVF as the method of choice for fertilizing the eggs. A single sperm is placed (injected) into each of the eggs retrieved by puncture using a fine injection pipette.
Cryopreservation
A surplus number of eggs from a stimulation cycle can be cryopreserved (frozen). In this way, stimulation as well as oocyte puncture can be omitted at a later stage. We also offer the possibility of freezing sperm and, for example, testicular tissue or ovarian tissue.
Luteal phase support
The luteal phase is the time during which progesterone is produced by the body. Luteal phase support is necessary when too little of the body's own progesterone is produced.
Myomas
Myomas are benign tumors of the muscle tissue of the uterus. They can occur in a wide variety of locations in the uterus and cause menstrual irregularities. Myomas can be the cause of infertility as well as the occurrence of miscarriages.
OAT syndrome
OAT stands for Oligo-Astheno-Teratozoospermia and means that too few, insufficiently mobile and increasingly malformed sperm are detectable in the ejaculate. The reason may be a malposition of the testis, the occurrence of varicose veins in the testicle (varicocele), a genetic disorder (e.g. Klinefelter's syndrome), a hormonal disorder or infection (e.g. Mumps-Orchitis). Chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy may also result in the development of OAT syndrome.
Oocyte
Female germ cell
Ovulation
The discharge of an oocyte from the ovarian follicle.
Ovulation induction
Refers to the triggering of ovulation. Hormone and ultrasound monitoring are used to determine the optimal time for triggering ovulation (performed by a hormone injection).
Polycystic ovary (PCO)
Derived from the Greek kytis = bladder and poly = numerous. Ovary with many small cysts, usually associated with elevated male hormones.
PCT
Is the abbreviation for postcoital test. This is an examination of the cervical canal mucus for the presence of sperm at the time of ovulation, the number and motility of sperm is examined.
PKD
Polar body diagnosis
A special chromosome analysis on the eggs. If artificial insemination with egg collection and fertilization in a test tube is planned, the eggs can be examined for chromosome maldistribution.
Sterility
If regular sexual intercourse does not result in pregnancy for more than a year, doctors assume infertility (sterility). However, this does not have to be definitive and can often be overcome with modern procedures in fertility medicine.
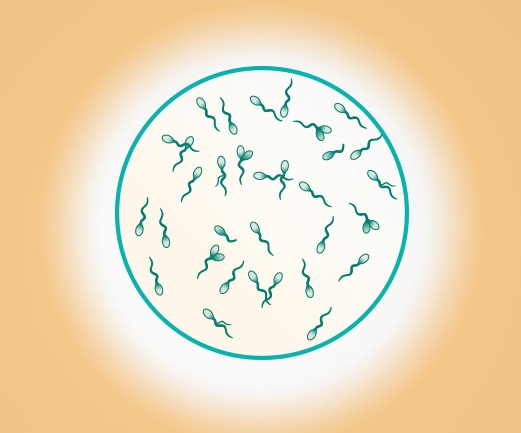
Sperm
Male germ cell
TESE
Testicular sperm extraction. Procedure for obtaining sperm cells from testicular tissue.
Hyperstimulation syndrome
Rare complication following ovarian stimulation by hormone treatment: greatly enlarged ovaries with water retention in the abdomen.
Zygote
A zygote is the term used after fusion of the genetic material from the egg and the sperm during fertilization.
Cycle monitoring
Monitoring of follicle and egg maturation by means of ultrasound and hormone blood tests.
Dresden Fertility Center
in the Wöhrl Plaza
Prager Str. 8a
01069 Dresden
Phone +49 351 501 400-0
Fax +49 351 501 400-28
Email:
Instagram Arrange your first appointment NEW: Video consultation! Downloads Impressions
Cryobank in the Kinderwunschzentrum Dresden
Prager Str. 8a
01069 Dresden
Tel. +49 351 50140019
E-Mail:
| Office hours | |
|---|---|
| Mon., Wed., Thu. | 08.00 – 19.00 Hrs |
| Tue. | 08.00 – 13.00 Hrs and 14.30 – 19.00 Hrs |
| Fri. | 08.00 – 14.00 Hrs |
Availability by telephone |
|
| Mon., Wed. | 08.00 – 13.00 Hrs and 14.30 – 18.00 Hrs |
| Tue., Thu., Fri. | 08.00 – 13.00 Hrs |
Blood sampling |
|
| Mon. - Thu. | 08.00 – 17.30 Hrs |
| Fri. | 08.00 – 13.30 Hrs |
On Tuesdays the clinic is closed from 13.00 to 14.30 Hrs! |
|
Service at the Fertility Center Dresden

To the planned child